05/02/2009
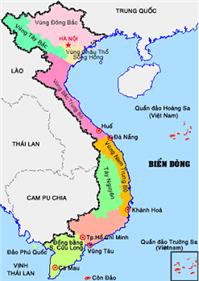
Vietnam is a long and narrow country, lying completely in the tropical zone. Its landmass forms the shape of the letter S on the east side of the Indochinese Peninsula in Southeast Asia. Vietnamese eastern border consists of more than 3,000 km of coastline, facing the East Sea and the Pacific Ocean. To the north, Vietnam shares its border with China, while to the west, with Cambodia and Laos.
Vietnam's S-shaped landmass widens in the north and in the south. Northern Vietnam has large plains lying in the river basins of the Red, Lo, and Chay Rivers, which flow in a northeast-to-southwest direction into Bac Bo Gulf. North and northwest of these plains are large hilly and mountainous areas. Northern Vietnam is influenced by a monsoon climate, with four distinct seasons and high humidity. In order to cultivate land and earn their living, inhabitants of the north built dikes over the centuries, resulting in today's system of dikes that are thousands of kilometers long along the river banks.
Southern Vietnam has the Mekong River, which originates in China, and flows through Laos and Cambodia before entering Vietnam. In Vietnam, the river splits into nine tributaries before flowing into the East Sea, which is the reason the Vietnamese call it the Cuu Long (Nine Dragons) River. The rich and fertile Mekong Delta region is the leading rice producer in the country. The south has only two seasons, the rainy season and the dry season.
Between these large delta regions in the north and south is the long and narrow Central Vietnam. In the west is the Truong Son mountain range. Short rivers running straight to the East Sea cross the region, creating small narrow plains along the coast. The climate of Central Vietnam is often harsh, and subject to natural calamities such as typhoons. In the southwestern part of Central Vietnam, there are large, high plateaus, 1,000 meters above sea level, with fertile basalt layers, appropriate for the cultivation of tropical and temperate cash crops, such as rubber, tea, coffee, and cacao.
Vietnamese long coastline has many beautiful beaches, and includes the famous Ha Long Bay, which has more than 3,000 small mountains on the sea and which was recognized by the United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) as a world heritage. Vietnam has many primitive areas of forest with precious timber, rare fauna, and high mountains with temperate climates which are very attractive for tourists. A large number of lakes, rivers, streams, waterfalls, and grottoes complete the beauty spots of Vietnam.
Vietnamese natural resources include coal, iron, bauxite, and precious stones, which are mined in northern and central Vietnam, and large reserves of oil and gas in the coastal areas and on the continental shelf.
Vietnam's S-shaped landmass widens in the north and in the south. Northern Vietnam has large plains lying in the river basins of the Red, Lo, and Chay Rivers, which flow in a northeast-to-southwest direction into Bac Bo Gulf. North and northwest of these plains are large hilly and mountainous areas. Northern Vietnam is influenced by a monsoon climate, with four distinct seasons and high humidity. In order to cultivate land and earn their living, inhabitants of the north built dikes over the centuries, resulting in today's system of dikes that are thousands of kilometers long along the river banks.
Southern Vietnam has the Mekong River, which originates in China, and flows through Laos and Cambodia before entering Vietnam. In Vietnam, the river splits into nine tributaries before flowing into the East Sea, which is the reason the Vietnamese call it the Cuu Long (Nine Dragons) River. The rich and fertile Mekong Delta region is the leading rice producer in the country. The south has only two seasons, the rainy season and the dry season.
Between these large delta regions in the north and south is the long and narrow Central Vietnam. In the west is the Truong Son mountain range. Short rivers running straight to the East Sea cross the region, creating small narrow plains along the coast. The climate of Central Vietnam is often harsh, and subject to natural calamities such as typhoons. In the southwestern part of Central Vietnam, there are large, high plateaus, 1,000 meters above sea level, with fertile basalt layers, appropriate for the cultivation of tropical and temperate cash crops, such as rubber, tea, coffee, and cacao.
Vietnamese long coastline has many beautiful beaches, and includes the famous Ha Long Bay, which has more than 3,000 small mountains on the sea and which was recognized by the United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) as a world heritage. Vietnam has many primitive areas of forest with precious timber, rare fauna, and high mountains with temperate climates which are very attractive for tourists. A large number of lakes, rivers, streams, waterfalls, and grottoes complete the beauty spots of Vietnam.
Vietnamese natural resources include coal, iron, bauxite, and precious stones, which are mined in northern and central Vietnam, and large reserves of oil and gas in the coastal areas and on the continental shelf.